Cholestero
Essential for Hormone Production: Cholesterol serves as a fundamental precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, enabling critical physiological processes.
Vitamin D Synthesis: It functions as a biochemical precursor for vitamin D synthesis, essential for maintaining bone integrity and immune function.
Bile Acid Formation: Cholesterol is metabolized into bile acids, facilitating intestinal emulsification and absorption of dietary lipids.
Universal Presence in Cells: As a ubiquitous component of cellular membranes, cholesterol ensures structural stability and modulates membrane fluidity.
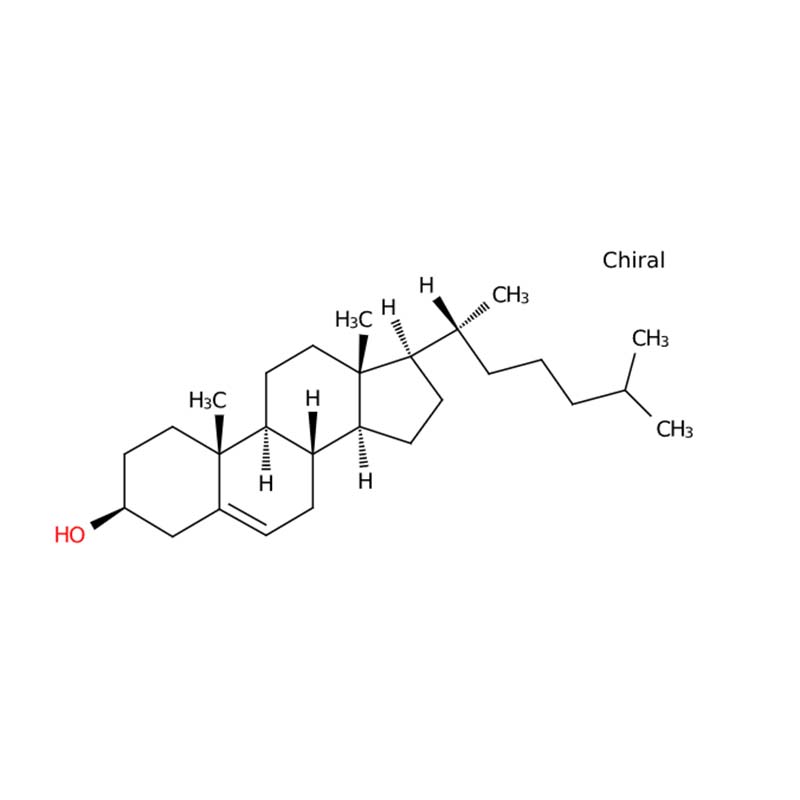
Cholesterol is a sterol compound with a waxy consistency that constitutes an integral component of all cellular membranes. While endogenously synthesized mainly in the liver, it can also be acquired through dietary sources. This lipid molecule functions as a vital precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids, supporting multiple essential physiological processes.
Cholesterol (CAS# 57-88-5) Product Applications:
Cholesterol serves as a critical raw material in biochemical research, particularly in studies involving brain phospholipids, cholesterol flocculation assays, and the synthesis of vitamin D and steroid hormones. It is also employed as a biochemical reagent and emulsifying agent across various industrial processes. Additionally, cholesterol finds application in pharmaceutical manufacturing, notably in the production of artificial bezoar and hormone-based medications, where it functions as an effective emulsifier in formulation systems.
Cholesterol Chemical Properties
Melting point | 148-150 °C |
alpha | -36 º (c=2, dioxane) |
Boiling point | 360 °C |
density | 1.06 |
refractive index | 1.5250 (estimate) |
Fp | 250 °C |
storage temp. | -20°C |
solubility | H2O: 0.002 mg/mL |
form | |
pka | 15.03±0.70(Predicted) |
color | white |
Specific Gravity | 1.067 |
Odor | wh. or faintly yel. pearly granules or crystals, almost odorless |
biological source | synthetic |
Optical Rotation | -40.201°(C=0.01g/ml CHCL3) |
Water Solubility | negligible |
Merck | 14,2201 |
BRN | 1915888 |
Dielectric constant | 2.9(Ambient) |
InChIKey | HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N |
LogP | 9.619 (est) |
CAS DataBase Reference | 57-88-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Cholesterol(57-88-5) |
IARC | 3 (Vol. 31, Sup 7) 1987 |
EPA Substance Registry System | Cholesterol (57-88-5) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi |
Risk Statements | 10-48/20/22-40-38-22-36/37/38-67-36/38-20-63 |
Safety Statements | 24/25-22-36/37-36-26 |
RIDADR | UN 1170 3/PG 3 |
WGK Germany | 1 |
RTECS | FZ8400000 |
TSCA | Yes |
HS Code | 2906 13 10 |
HazardClass | IRRITANT |
Hazardous Substances Data | 57-88-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | Present in all parts of the animal body; concentrated in spinal cord, brain, skin secretions, and gallstones. An unsaturated, unsaponifiable alcohol (m.p. 149℃). It is synthesized in the body from ethanoate units; its metabolism is regulated by a specific set of enzymes. It is the parent compound of many other steroids and its presence in high concentrations in the blood is suspected as being a contributory factor in cardiovascular disease. |