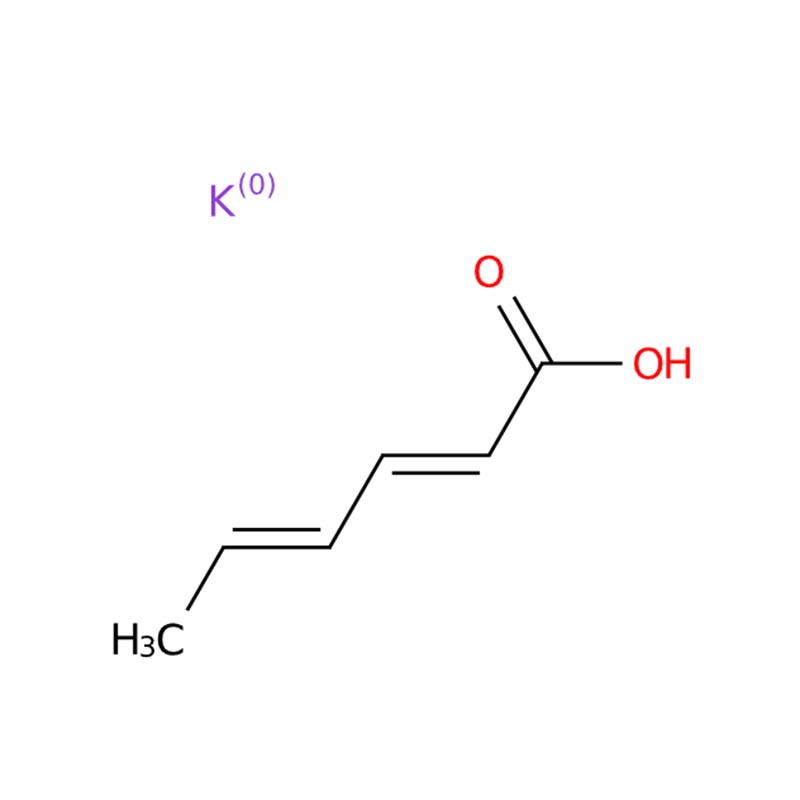
Potassium Sorbate
Effective Preservative: Prevents the proliferation of mold and yeast in food items, extending shelf life.
Biodegradable: Fully decomposes in the environment, aligning with natural fatty acid degradation pathways.
Versatile Origin: Initially sourced from plants, now consistently manufactured via synthetic routes for reliable supply.
Stable White Crystalline Form: Easily handled and uniformly blended into product formulations due to its consistent physical state.
Potassium sorbate presents as a white crystalline powder and functions as the potassium salt derivative of sorbic acid. Initially identified in the 1850s from extracts of the Mountain Ash Tree, it is currently manufactured through synthetic methods. This compound serves as an efficient food preservative, exhibiting biodegradable characteristics and a molecular structure resembling natural fatty acids. Its preservative action is achieved through suppressing the development of molds and yeasts in food products.
Potassium sorbate Chemical Properties
Melting point | 270 °C |
Density | 1,361 g/cm3 |
Vapor pressure | <1 Pa (20 °C) |
FEMA | 2921 | POTASSIUM SORBATE |
Storage temp | 2-8°C |
Solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless to faintly yellow |
Form | Powder |
Pka | 4.69[at 20 ℃] |
Color | White to light cream |
Odor | Odorless |
PH Range | 8 - 11 at 580 g/l at 20 °C |
PH | 7.8 (H2O, 20.1℃) |
Water Solubility | 58.2 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
Merck | 14,7671 |
BRN | 5357554 |
Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
InChIKey | CHHHXKFHOYLYRE-STWYSWDKSA-M |
LogP | -1.72 at 20℃ |
CAS DataBase Reference | 24634-61-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium sorbate (24634-61-5) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | Xi,C,T,F |
Risk Statements | 36/37/38-35-22 |
Safety Statements | 26-36-45-36/37/39 |
WGK Germany | 1 |
RTECS | WG2170000 |
Autoignition Temperature | >150 °C |
TSCA | Yes |
HS Code | 2916 19 95 |
Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 3800 mg/kg |
When dissolved in water, potassium sorbate dissociates into sorbic acid, demonstrating broad-spectrum efficacy against yeasts, molds, and select bacteria. It is typically applied at concentrations of 250–1000 ppm across diverse food categories, including dairy products, baked goods, beverages, condiments, and preserved foods. This makes it a versatile and widely adopted food preservative.