Lead(II) Carbonate Basic
Ambient Stability: Maintains structural integrity under standard temperature and pressure conditions, ensuring consistent performance during storage and handling.
Controlled Thermal Decomposition: Exhibits predictable breakdown patterns at elevated temperatures, enabling precise management in thermal processing applications.
Selective Solubility Profile: Demonstrates dissolution capabilities in strong acids including acetic and nitric acid systems, facilitating versatile chemical processing.
Hydrogen Sulfide Reactivity: Undergoes progressive reaction with H₂S to generate a distinctive black compound, applicable in specialized industrial processes and detection methodologies.
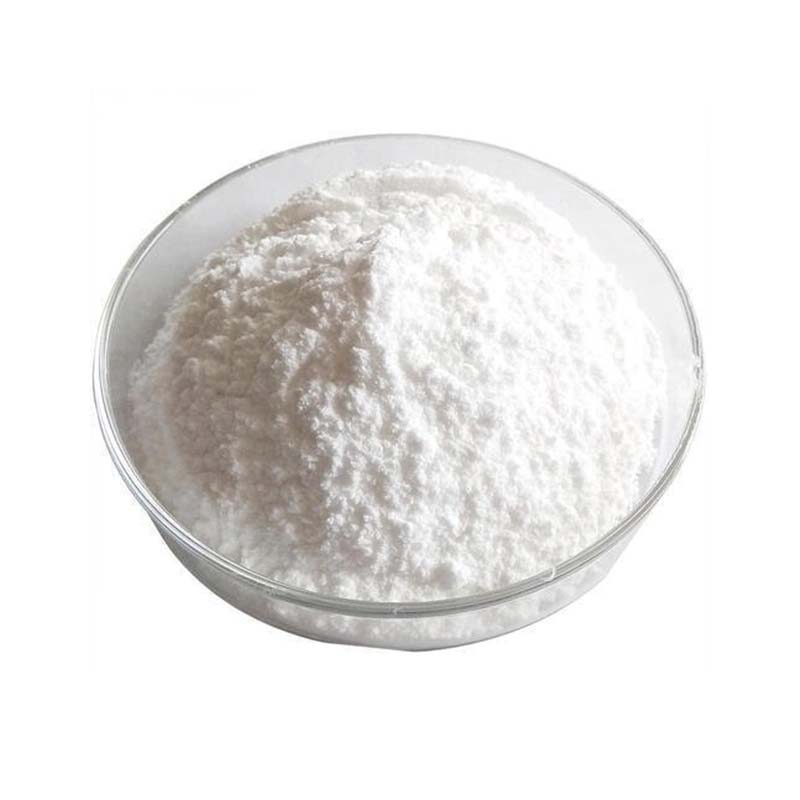
Basic lead carbonate presents as a dense white powder with a hexagonal crystalline structure. This compound demonstrates insolubility in both water and ethanol, while showing ready solubility in strong acids including acetic acid and nitric acid. It maintains chemical stability under standard temperature and pressure conditions. When subjected to heating at 220°C for four hours, approximately 9% of its carbon dioxide content decomposes, resulting in the conversion of 95% of the substance into 2PbCO₃·PbO. Further decomposition occurs at 400°C, producing lead oxide with concurrent release of carbon dioxide. Exposure to hydrogen sulfide induces gradual blackening through the formation of 4PbCO₃·PbS·Pb(OH)₂.

Lead(II) carbonate basic Chemical Properties
Melting point | 400 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
Density | 6,14 g/cm3 |
Solubility | insoluble in H2O, ethanol; soluble in acid solutions |
Form | Powder |
Specific Gravity | 6.14 |
Color | White to off-white |
Water Solubility | Insoluble |
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 13.13 |
Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3 |
Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. |
InChI | InChI=1S/2CH2O3.2H2O.3Pb/c2*2-1(3)4;;;;;/h2*(H2,2,3,4);2*1H2;;;/q;;;;3*+2/p-6 |
InChIKey | RYZCLUQMCYZBJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-H |
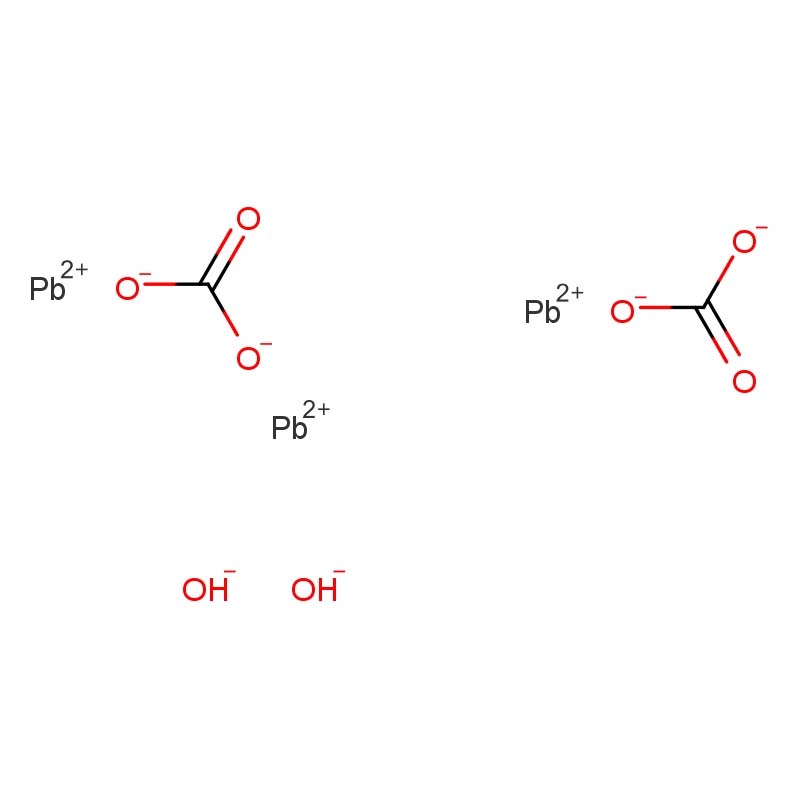
SMILES | C([O-])([O-])=O.C([O-])([O-])=O.[Pb](O)O.[Pb+2].[Pb+2] |
CAS DataBase Reference | 1319-46-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Basic lead carbonate (1319-46-6) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | T,N |
Risk Statements | 61-20/22-33-50/53-62 |
Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 |
RIDADR | UN 2291 6.1/PG 3 |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | OF9275000 |
TSCA | Yes |
HazardClass | 6.1 |
PackingGroup | III |
HS Code | 28369917 |
Hazardous Substances Data | 1319-46-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |

Basic lead carbonate exhibits a high refractive index and demonstrates exceptional weather resistance, enabling its broad utilization in pigments, coatings, plastics, printing, dyeing processes, and analytical reagents. Within the pigment industry, it is particularly valued for producing premium pearlescent pigments and serves as a key component in inorganic paint and coating formulations. For printing and ink applications, it is effectively employed on diverse substrates including packaging paper, business cards, plastic fabrics, and textile materials.