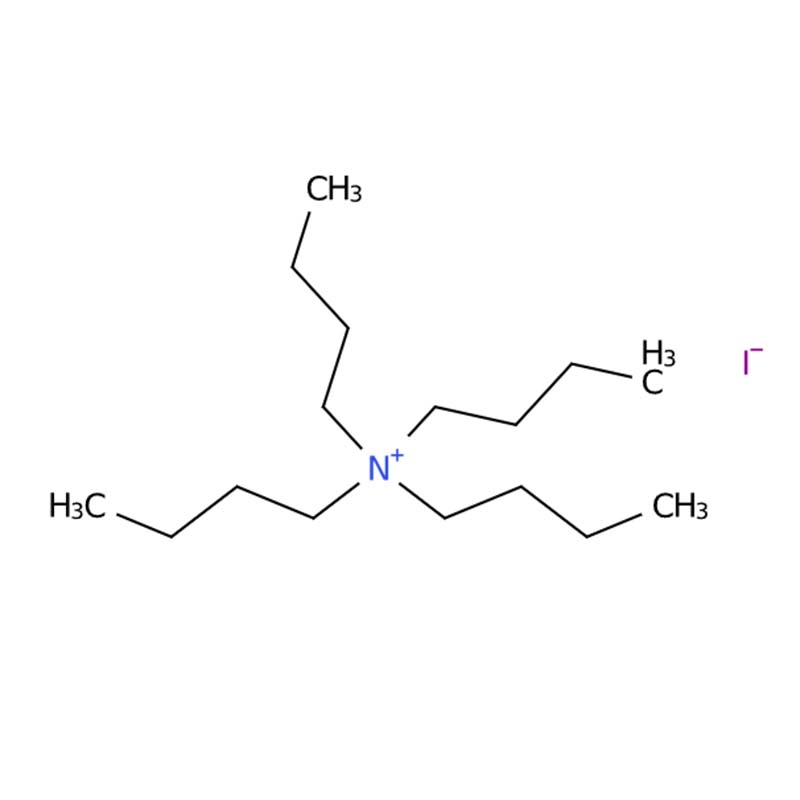
Tetrabutylammonium iodide
Highly Efficient Catalyst: Tetrabutylammonium iodide (TBAI) functions as an effective phase-transfer catalyst that significantly accelerates reaction rates.
Cost-Effective Iodine Source: It enables in-situ iodide generation, reducing dependence on unstable or expensive iodide reagents.
Versatile Application: The compound demonstrates broad utility across diverse chemical reactions, enhancing process flexibility.
Specialized Use in Dealkylation: Particularly effective for dealkylation reactions of esters and ethers, improving both efficiency and yield.
Tetrabutylammonium iodide (TBAI) serves as an efficient phase-transfer catalyst that improves reaction kinetics and enables diverse chemical transformations. It functions as an iodine source through in-situ iodide generation, providing a stable alternative to conventional iodide reagents. The compound is particularly effective in dealkylation processes involving esters and ethers.
Tetrabutylammonium iodide Chemical Properties
Melting point | 141-143 °C(lit.) |
Boiling point | 145.3℃[at 101 325 Pa] |
Density | 1.20 |
Vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
Storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
Solubility | Acetonitrile: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
Form | Crystalline Powder |
Color | White to cream |
Odor | Amine like |
Water Solubility | Soluble in water and methanol. Insoluble in benzene. |
Sensitive | Light Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
λmax | λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.1 |
BRN | 3916152 |
Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 ppm |
Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Light-sensitive. |
InChIKey | DPKBAXPHAYBPRL-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
LogP | 0.869 at 25℃ |
CAS DataBase Reference | 311-28-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Tetrabutylammonium iodide (311-28-4) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | Xn |
Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38 |
Safety Statements | 26-36-37/39 |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | BS5450000 |
F | 8 |
TSCA | Yes |
HS Code | 29239000 |
Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 1990 mg/kg |
As a phase transfer catalyst, TBAI effectively mediates the alkylation of nucleophilic substrates including alcohols, amines, and phospholipids under mild conditions. Its catalytic performance proves particularly essential in biphasic reaction environments, where it significantly enhances reaction kinetics and product formation.