Cellulase
Efficient Cellulose Hydrolysis: Catalyzes the controlled enzymatic degradation of cellulose into glucose and low-polymer oligosaccharides, supporting efficient biomass conversion.
Multi-Component Synergy: Integrates endoglucanase, exoglucanase, and cellobiase in an optimized formulation that enables efficient cellulose degradation through synergistic action.
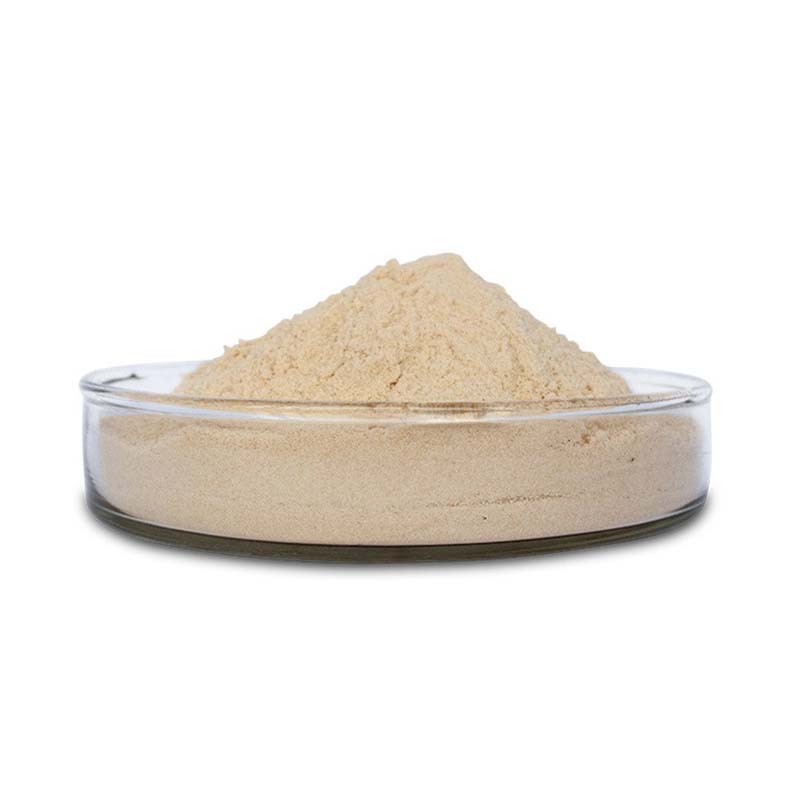
Versatile Form: Provided as an off-white powdered concentrate or ready-to-use liquid, offering flexible handling and dosing for different process requirements.
Extensive Application Potential : Its broad catalytic properties make it useful across many biochemical and industrial processes.
Cellulase refers to a complex of enzymes responsible for breaking down cellulose into glucose and short-chain oligosaccharides. This enzymatic system is composed primarily of endoglucanase, exoglucanase, and β-glucosidase, which act in coordination rather than functioning as a single enzyme. Commercial cellulase is typically supplied either as a light-colored powder or in liquid form.
English name | Cellulase |
English synonyms | Celluase;cellulasefromtrichodermalongibrachia-tum;qianweimeis;Fungalcellulase;1,4-[1,3:1,4]-BETA-D-GLU CAN;1,4-[1,3:1,4]-BETA-D-GLUCAN 4-GLUCANO-HYDROLASE;IUB: 3.2.1.4;MEICELASE |
CAS number | 9012-54-8 |
Molecular formula | NULL |
Molecular weight | 0 |
EINECS number | 232-734-4 |
Density | 1.2 g/mL at 25°C |
Vapor Pressure | 0.004 Pa at 25°C |
Storage Conditions | 2-8°C |
Solubility | Solubility in deionized water is 5.0 mg/mL (sterile; in the presence of 0.15% polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB)). |
Form | Powder |
Color | White |
Cellulase has broad applications across numerous industries, such as textiles, detergents, papermaking, food fermentation, industrial cleaning, tobacco processing, oil extraction, wastewater treatment, and animal feed. In nature, these enzymes are produced by microorganisms, certain insects, and plants. Within seeds, cellulase helps break down the cellulose of the seed coat, supporting germination. In herbivorous ruminants, symbiotic microorganisms in the digestive system release cellulase to convert cellulose into digestible sugars. In research and production, cellulase preparations are essential tools for plant protoplast isolation. Enzymes used in industry are typically endo-glucosidases that feature both a catalytic region and a cellulose-binding domain, enabling efficient cellulose degradation.