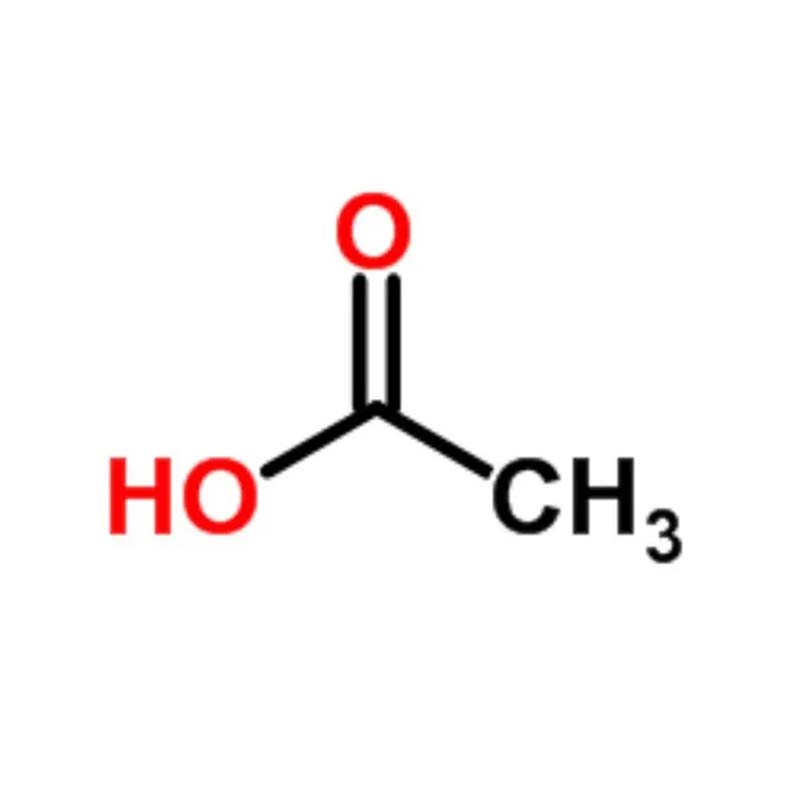
Acetic acid ( Industrial Grade)
High Purity & Stability: Supplied as “glacial acetic acid,” which solidifies at approximately 16.6°C, reflecting high purity and concentration ideal for precision applications. Remains stable when stored below 30°C.
Excellent Solubility: Exhibits full miscibility with water, ethanol, glycerol, and ether, enabling versatile formulation across chemical synthesis and product development.
Versatile Weak Organic Acid: Acts as a mild acid catalyst (pKa ≈ 4.74) with lower corrosivity than mineral acids, effectively facilitating key processes such as esterification.
Wide Industrial Utility: Serves as a foundational chemical feedstock in the manufacture of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), acetic anhydride, esters (for solvents and flavors), pharmaceuticals, and textiles, supported by established safe-handling practices.
Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid (AcOH), is a fundamental fatty acid best known as the main acidic component of vinegar. It occurs naturally in many plants, either in free form or esterified, and has the molecular formula CH₃COOH. The use of vinegar dates back millennia, with historical evidence of production in ancient China. Concentrated acetic acid was first isolated by Stahl in 1700.
Pure acetic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It has a melting point of 16.6 °C, a boiling point of 117.9 °C, and a relative density of 1.049 at 20 °C. It is miscible with water, ethanol, glycerol, ether, and carbon tetrachloride, but insoluble in carbon disulfide. In its anhydrous form, it solidifies at low temperatures into ice-like crystals, hence the name “glacial acetic acid.” It is corrosive and behaves as a weak organic acid (pKa = 4.76), displaying typical acid characteristics such as participating in esterification reactions with alcohols.
Acetic acid Chemical Properties
Melting point | 16.2 °C(lit.) |
Boiling point | 117-118 °C(lit.) |
density | 1.049 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
vapor density | 2.07 (vs air) |
vapor pressure | 11.4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
refractive index | n20/D 1.371(lit.) |
FEMA | 2006 | ACETIC ACID |
Fp | 104 °F |
storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
solubility | alcohol: miscible(lit.) |
form | Solution |
pka | 4.74(at 25℃) |
Specific Gravity | 1.0492 (20℃) |
color | colorless |
Odor | Strong, pungent, vinegar-like odor detectable at 0.2 to 1.0 ppm |
PH | 3.91(1 mM solution);3.39(10 mM solution);2.88(100 mM solution); |
PH Range | 2.4 (1.0M solution) |
Odor Threshold | 0.006ppm |
Odor Type | acidic |
explosive limit | 4-19.9%(V) |
Water Solubility | miscible |
λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 |
Merck | 14,55 |
JECFA Number | 81 |
BRN | 506007 |
Henry's Law Constant | 133, 122, 6.88, and 1.27 at pH values of 2.13, 3.52, 5.68, and 7.14, respectively (25 °C, Hakuta et al., 1977) |
Dielectric constant | 4.1(2℃) |
Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 ppm ~25 mg/m3) (ACGIH, OSHA, and MSHA); TLV-STEL 15 ppm (37.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
Stability: | Volatile |
LogP | -0.170 |
CAS DataBase Reference | 64-19-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid(64-19-7) |
EPA Substance Registry System | Acetic acid (64-19-7) |
Safety Information
Hazard Codes | C,Xi |
Risk Statements | 34-42-35-10-36/38 |
Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-45-23-24/25 |
RIDADR | UN 1792 8/PG 2 |
WGK Germany | 3 |
RTECS | NN1650000 |
F | 1-8-10 |
Autoignition Temperature | 426 °C |
TSCA | Yes |
HazardClass | 8 |
PackingGroup | II |
HS Code | 29152100 |
Hazardous Substances Data | 64-19-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Toxicity | LD50 in rats (g/kg): 3.53 orally (Smyth) |
IDLA | 50 ppm |